Leadership Agility
Quick Reference Guide to Five Levels of Leadership Agility
Level of Agility |
View of Leadership |
Agility in Pivotal Conversations |
Agility in Leading Teams |
Agility in Leading Organizational Change |
Heroic levels |
||||
Pre-expert (~10%) |
||||
Expert (~45%) |
Tactical, problem-solving orientation. Believes that leaders are respected and followed by others because of their authority and expertise. |
Style is either to strongly assert opinions or hold back to accommodate others. May swing from one style to the other, articularly for different relationships. Tends to avoid giving or requesting feedback. |
More of a supervisor than a manager. Creates a group of individuals rather than a team. Work with direct reports is primarily one-on-one. Too caught up in the details of own work to lead in a strategic manner. |
Organizational initiatives focus primarily on incremental improvements inside unit boundaries with little attention to stakeholders. |
Achiever (~35%) |
Strategic outcome orientation. Believes that leaders motivate others by making it challenging and satisfying to contribute to larger objectives. |
Primarily assertive or accommodative with some ability to compensate with the less preferred style. Will accept or even initiate feedback, if helpful in achieving desired outcomes. |
Operates like a full-fledged manager.Meetings to discuss important strategic or organizational issues are often orchestrated to try to gain buy-in to own views. |
Organizational initiatives include analysis of industry environment. Strategies to gain stakeholder buy-in range from one-way communication to soliciting input. |
Post-heroic levels |
||||
Catalyst (~5%) |
Visionary, facilitative orientation. Believes that leaders articulate an innovative, inspiring vision and bring together the right people to transform the vision into reality. Leaders empower others and actively facilitate their development. |
Adept at balancing assertive and accommodative styles as needed in particular situations. Likely to articulate and question underlying assumptions. Genuinely interested in learning from diverse viewpoints. Proactive in seeking and applying keep as is feedback. |
Intent on creating a highly participative team. Acts as a team leader and facilitator. Provides and seeks open exchange of views on difficult issues. Empowers direct reports. Uses team development as a vehicle for leadership development. |
Organizational initiatives often include development of a culture that promotes teamwork, participation, and empowerment. Proactive engagement with diverse stakeholders reflects a belief that their input increases the quality of decisions, not just buy-in. |
Co-creator (~4%) |
Oriented toward shared purpose and collaboration. Believes leadership is ultimately a service to others. Leaders collaborate with other leaders to develop a shared vision that each experiences as deeply purposeful. |
Integrates assertive and accommodative sides in pivotal conversations and is agile in using both styles. Able to process and seriously consider negative feedback even when highly charged emotionally. |
Develops a collaborative leadership team, where members feel full responsibility not only for their own areas but also for the unit or organization they collectively manage. Practical preference for consensus decision making but doesn't hesitate to use authority as needed. |
Develops key stakeholder relationships characterized by deep levels of mutual influence and genuine dedication to the common good. May create companies or organizational units where corporate responsibility and deep collaboration are integral practices. |
Synergist (~1%) |
Holistic orientation. Experiences leadership as participation in a palpable life purpose that benefits others while serving as a vehicle for personal transformation. |
Centered "within" not "with" assertive and accommodative energies, expressed as appropriate to the situation. Cultivates a present-centered awareness that augments external feedback and supports a strong, subtle connection with others, even during challenging conversations. |
Capable of moving fluidly between various team leadership styles uniquely suited to the situation at hand. Can shape or amplify the energy dynamics at work in a particular situation to bring about mutually beneficial results. |
Develops and maintains a deep, empathetic awareness of conflicting stakeholder interests, including the leader's own. Able to access synergistic intuitions that transform seemingly intractable conflicts into solutions beneficial for all parties involved. |
Leadership Agility Compass
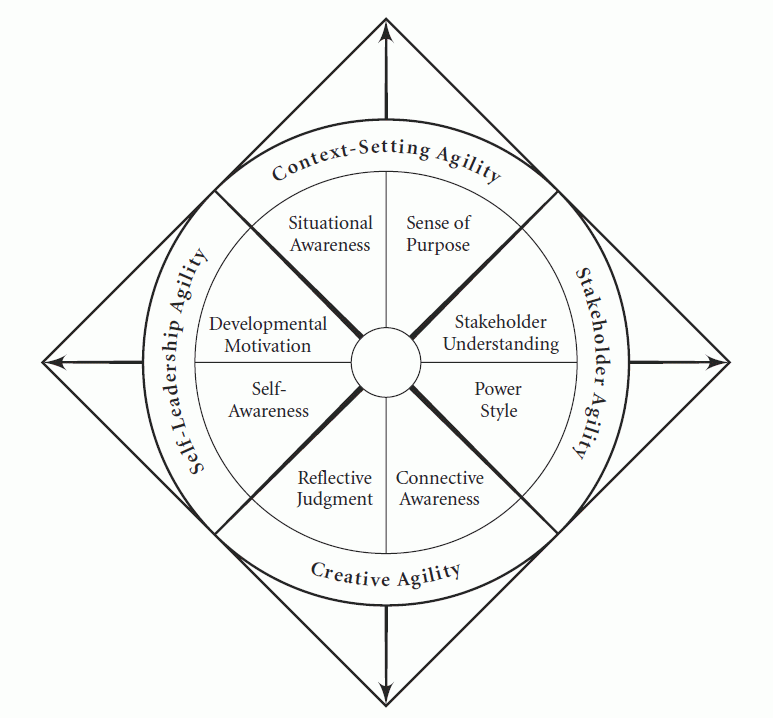
Context-setting agility improves your ability to scan your environment, frame the initiatives you need to take, and clarify the outcomes you need to achieve.
Stakeholder agility increases your ability to engage with key stakeholders in ways that build support for your initiative.
Creative agility enables you to transform the problems you encounter into the results you need.
Self-leadership agility is the ability to use your initiatives as opportunities to develop into the kind of leader you want to be.3
5가지 level * 4개 분야 = 20가지 분야별 level에 대해서 설명한다.
조직의 Creativity를 위해서는 Agile한 조직이 필요하다.